What is protein electrophoresis? Protein electrophoresis is a standard laboratory technique in which charged protein molecules are transported through a solvent by an electric field. Both proteins and nucleic acids can be separated by electrophoresis, a simple, fast and sensitive analytical tool.
What are polyacrylamide gels? Polyacrylamide is the material of choice for preparing electrophoretic gels to separate proteins by size. Polyacrylamide gels are prepared by mixing acrylamide with bisacrylamide to form a cross-linked polymer network when the polymerizing agent, ammonium persulfate (APS), is added.
In SDS-PAGE, the gel is poured into a buffer containing sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), an anionic detergent. SDS denatures proteins by wrapping the polypeptide backbone. By heating the protein sample to 70-100°C in the presence of excess SDS and thiol reagent, the disulfide bonds are cleaved and the protein completely dissociates into its subunits.
Western blot (immunoblot) is a widely used method for protein detection and identification of specific proteins in protein solution in areas such as protein biology, immunogenetics, and molecular biology.
Western blot technique combines the specificity of antibody detection with the resolution of gel electrophoresis.
Western Blotting Steps: Sample preparation, Gel electrophoresis, Transfer of proteins to membrane, Antibody incubation, Imaging and analysis
How is Western Blot applied?
Colorimetric, chemiluminescent, fluorescent identification in protein identification
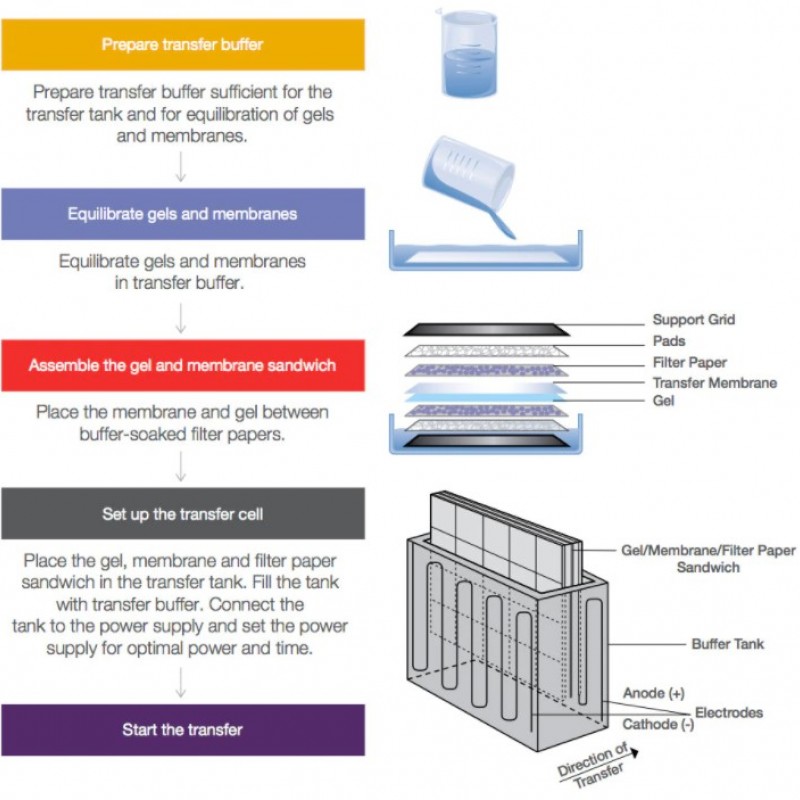
One of the key steps in the western blot workflow is the transfer of proteins from the polyacrylamide gel after electrophoresis to a nitrocellulose or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane so that specific proteins can be detected using immunosensing techniques.
Three main ways to manufacture proteins from SDS-PAGE or natural gels to nitrocellulose, PVDF or nylon membranes: